What is child Dentistry?
Children have two sets of teeth, milk teeth and permanent teeth. Both sets of teeth are important for children's speech, chewing, and for appearance. Additionally, milk teeth help in the proper development of muscles for chewing, and they also maintain the space so that permanent teeth can erupt in their correct positions.
The first tooth appears in your child's mouth at the age of 6 months. Parents are required to begin brushing these teeth to prevent them from decaying. All the milk teeth erupt in the mouth by the age of 2 – 3 years. There are 20 milk teeth. Parents must clean their child's teeth, as the child will be unable to do so. The child should gradually be taught to brush his/her own teeth as soon as they have learnt to spit out the toothpaste.
These teeth are shed between the age of 7 and 12 years, and are replaced by permanent teeth. But we have 32 permanent teeth, and the additional 12 permanent teeth erupt behind the milk teeth. The first one of these erupts at the age of 6 years, and is called the first permanent molar. This is a very important tooth.
All permanent teeth erupt by the age of 14 years, except the wisdom teeth, which usually erupts between the age of 17 and 25 years. So, between the age of 6 and 12 years, a child has both milk and permanent teeth. This is called the mixed dentition stage. Parents of these children often mistakenly think that the teeth, though decayed, do not require treatment and will fall off, as they will be replaced with new teeth.

Teething Problems
Many parents think that the fever and diarrohea, children get while the teeth are erupting is because of the eruption. This is only a coincidence. At that age, children are very active and tend to put everything into their mouth. This causes infection around the erupting teeth and upsets the stomach.
Double Teeth
Usually the permanent teeth are located just below their milk predecessors. With pressure from the permanent tooth, the root of the milk tooth gets dissolved / eaten away, and the milk tooth then falls to make way for the permanent tooth. But if the permanent tooth is placed too far away, it will erupt even without the predecessor falling, as there is no obstruction, and then we see double teeth, a new tooth behind or by the side of the old one. Such a situation should not be allowed to remain for long, say more than a couple of weeks. Timely removal of the milk tooth in such a case will allow the permanent tooth to take its rightful place.
Correcting the Alignment
The age for correction of alignment differs from case to case, but in general, it is best done after the child has completed 12 years and all the permanent teeth have erupted. Many times early commencement of treatment gives better results, but treatment is possible at an older age also. The right person to consult is an orthodontist.

Habit Breaking Appliances :
What are the different habits that can be encountered in children?
This can be thumb sucking, finger biting, nail biting, lip biting, mouth breathing, tongue thrusting etc.,


What are habit breaking appliances?
These are appliances that are made by a dentist to combat the above mentioned habits in children. They can be either a fixed or removable type.
What are the deleterious effects of these habits?
If these habits are continued for a prolonged period of time that can result in gum disease, change in position of teeth and change in shape of the jaws.
Is there any ideal age when these habits can be corrected?
No. whenever the habit is first noticed it is better to consult a dentist. He may give suggestions depending upon the habit
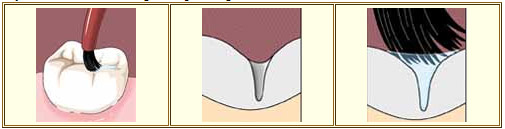
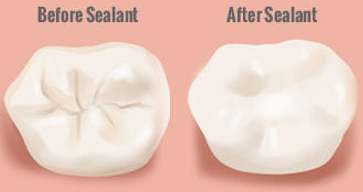
Pit and Fissure Sealants :
The top surfaces of your teeth - where the chewing takes place - aren't smooth and flat. They are cris-crossed with tiny hills and valleys - called pits and fissures. These are places where plaque can build up safe from your toothbrush and dental floss. Some of the pits and fissures are so narrow that even a single bristle from your toothbrush can't get deep enough to clean them out.
One method of preventing cavities from developing in the pits and fissures is to seal them off with a special varnish called a pit and fissure sealant.
Fluoride Treatment :
Fluoride naturally presents in teeth and it gives strength to teeth along with preventing teeth from decaying. Hence dentist all over the world suggest using such toothpastes that has fluoride in it. Fluoride also exists in water, eggs, fish, meat and tea. Out of which water has limited amount of fluoride. Fluoride is widely used in various dental treatments, in toothpastes and in mouth rinses. The dentists use various fluoride treatments to deal with tooth decaying.
Why is fluoride used in dentistry?
Fluoride is a key factor in preventive dental care for people of all ages. In fact, inadequate exposure to fluoride places children and adults in the high risk category for dental decay.
- • It acts on the tooth making the enamel harder and thus more resistant to acid.
- • It acts on the plaque, reducing its ability to make acid.
- • It promotes repair of tooth enamel
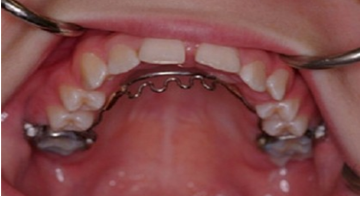
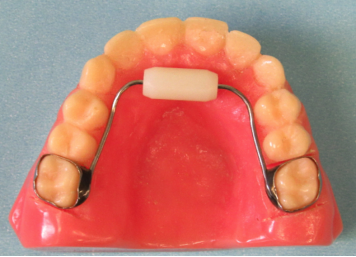
Space Maintainer :
Space maintainers are appliances made of metal or plastic that are custom fit to your child's mouth. They are small and unobtrusive in appearance. Most children easily adjust to them after the first few days. Space maintainers hold open the empty space left by a lost tooth. They steady the remaining teeth, preventing movement until the permanent tooth takes its natural position in the jaw. It's more affordable -- and easier on your child -- to keep teeth in normal positions with a space maintainer than to move them back in place with orthodontic treatment.
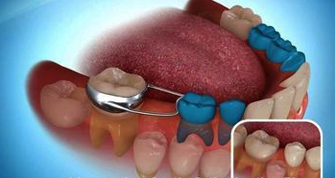
Pediatric dentists have four rules for space maintainer care.
First, avoid sticky sweets or chewing gum.
Second, don't tug or push on the space maintainer with your fingers or tongue.
Third, keep it clean with conscientious brushing and flossing.
Fourth, continue regular dental visits.
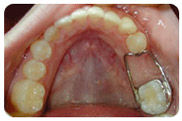
Nursing Bottle caries
Decay in infants and children is called Nursing bottle caries. It can destroy the teeth and most often occurs in the upper front teeth. But other teeth may also be affected.
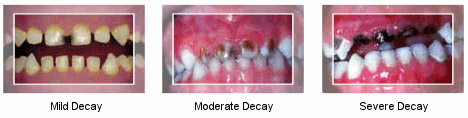
What causes Nursing bottle caries?
As soon as a baby's first teeth appear—usually by age six months or so—the child is susceptible to decay. Decay occurs when sweetened liquids are given and are left clinging to an infant's teeth for long periods. Many sweet liquids cause problems, including milk, formula and fruit juice. Bacteria in the mouth use these sugars as food. They then produce acids that attack the teeth. Each time your child drinks these liquids, acids attack for 20 minutes or longer. After many attacks, the teeth can decay.
It's not just what you put in your child's bottle that causes decay, but how often — and for how long a time. Giving your child a bottle of sweetened liquid many times a day should be avoided. Allowing your child to fall asleep with a bottle during naps or at night can also harm the child's teeth.
Guidelines for Preventing Tooth Decay
- • Sometimes parents do not realize that a baby's teeth can decay soon after they appear in the mouth. By the time decay is noticed, it may be too late to save the teeth. You can help prevent this from happening to your child by following the tips below:
- • After each feeding, wipe the baby's gums with a clean gauze pad. Begin brushing your child's teeth when the first tooth erupts. Clean and massage gums in areas that remain toothless, and begin flossing when all the baby teeth have erupted, usually by age 2 or 2½.
- • Never allow your child to fall asleep with a bottle containing milk, formula, fruit juice or sweetened liquids.
- • If your child needs a comforter between regular feedings, at night, or during naps, give the child a clean pacifier recommended by your dentist or physician. Never give your child a pacifier dipped in any sweet liquid.
- • Avoid filling your child's bottle with liquids such as sugar water and soft drinks.
- • If you’re local water supply does not contain fluoride (a substance that helps prevent tooth decay), ask your dentist how your child should get it.
- • Start dental visits by the child's first birthday. Make visits regularly. If you think your child has dental problems, take the child to the dentist as soon as possible.
- • Over 40 percent of children already have one or more cavities.
Risk factors include :
- • not brushing well
- • drinking too much juice and milk
- • eating a lot of junk food
- • not visiting a dentist regularly
- • getting a bottle or cup at night
Encourage Brushing & Flossing
- • Brushing twice a day and flossing are necessary to maintain healthy teeth and gums.
- • A pea-sized amount of fluoride toothpaste for children two and older is all that is needed.
- • Make sure your child spits out the toothpaste rather than swallowing it.
- • For young children, select a child-size toothbrush with soft bristles.
- • Children should be able to brush alone by age seven.
- • Replace toothbrushes every three to four months.
- • Replace toothbrushes every three to four months.
- • Ask your dentist or hygienist to demonstrate proper brushing and flossing techniques.
- • Supervise your child’s brushing and flossing until you are satisfied they are doing both properly.
- • Begin regular dental check-ups every six months.
- • Schedule the dental appointment for a time when your child feels rested & cooperative. Avoid nap and mealtimes if possible.
- • Don’t let anyone tell your child scary stories about dental visits.
- • Don’t let your child know if you feel any anxiety about going to the dentist.
- • Don’t bribe your child to go to the appointment.
- • Never use a dental visit as a punishment or threat.
- • Do try to make your child’s dental visit an enjoyable outing.
- • Set a good example by taking care of your oral hygiene and health
